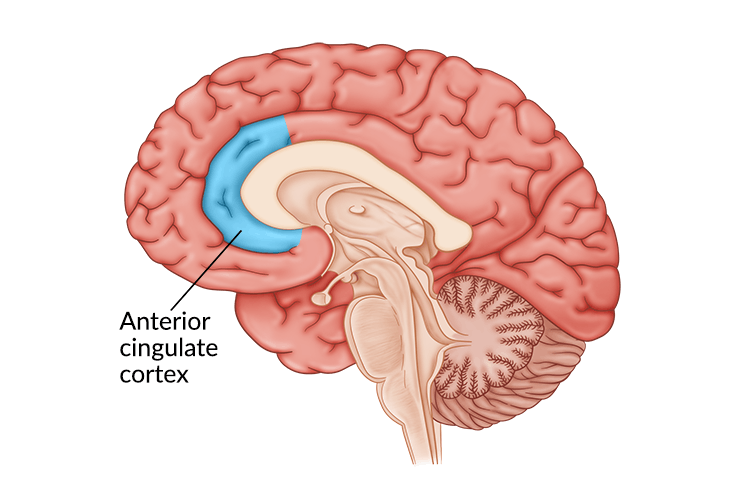
The cingulate cortex is a part of the brain situated in the medial aspect of the cerebral cortex. The cingulate cortex includes the entire cingulate gyrus, which lies immediately above the corpus callosum, and the continuation of this in the cingulate sulcus. The cingulate cortex is usually considered part of the limbic system.
It divides into four functionally distinct regions:
- anterior cingulate cortex (ACC)
- midcingulate cortex (MCC)
- posterior cingulate cortex (PCC)
- retrosplenial cortex.
The functional importance of human ACC and MCC was first highlighted by studies of patients with ACC and/or MCC lesions, who were reported to suffer from diverse symptoms, including apathy, as well as dysregulation of autonomic functions, emotion, attention, and error monitoring.
In the past few decades, neuroimaging work has expanded on these initial findings, demonstrating that ACC serves as a processing hub for the regulation of autonomic responses, as well as assessing emotional and motivational aspects of internal and external information. For instance, emotional contexts such as seeing emotional faces or listening to emotionally charged voices, reliably activate ACC. Consistent with ACC’s strong interconnection with autonomic brainstem nuclei, one of the most robust findings across species is that electrical stimulation of ACC depresses autonomic activity, leading to reduced blood pressure/heart rate, and respiratory inhibition.
MCC, by contrast, has been highlighted to play a role in different facets of cognitive control, such as response selection, attentional processing, monitoring conflict, and detecting errors. MCC’s role in decision-making seems to be especially pronounced in reward-based decision-making. Given the strong activation of this area in a multitude of task domains, an overarching theory is difficult to establish and has been the topic of intense debate. Overall, MCC activity seems to relate to multiple aspects of updating beliefs and internal models of the environment to guide decision-making.
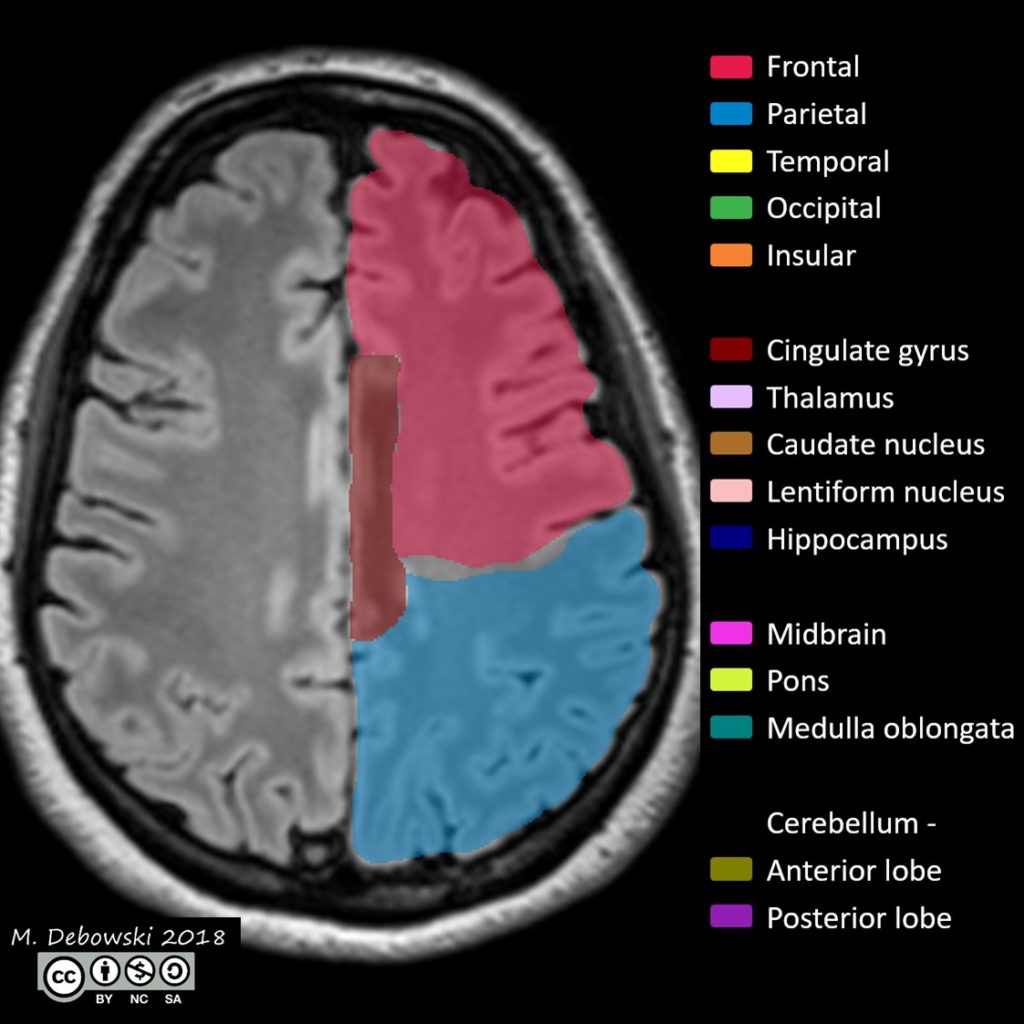
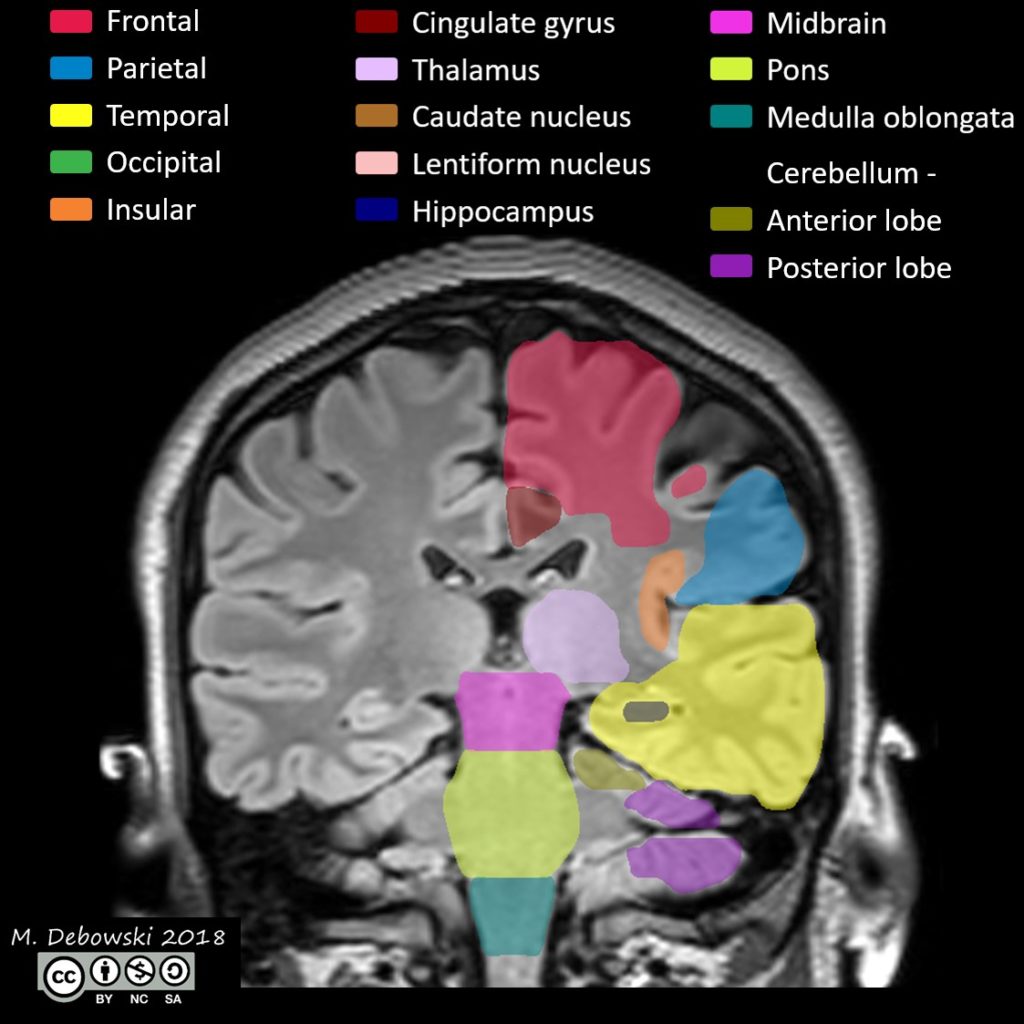
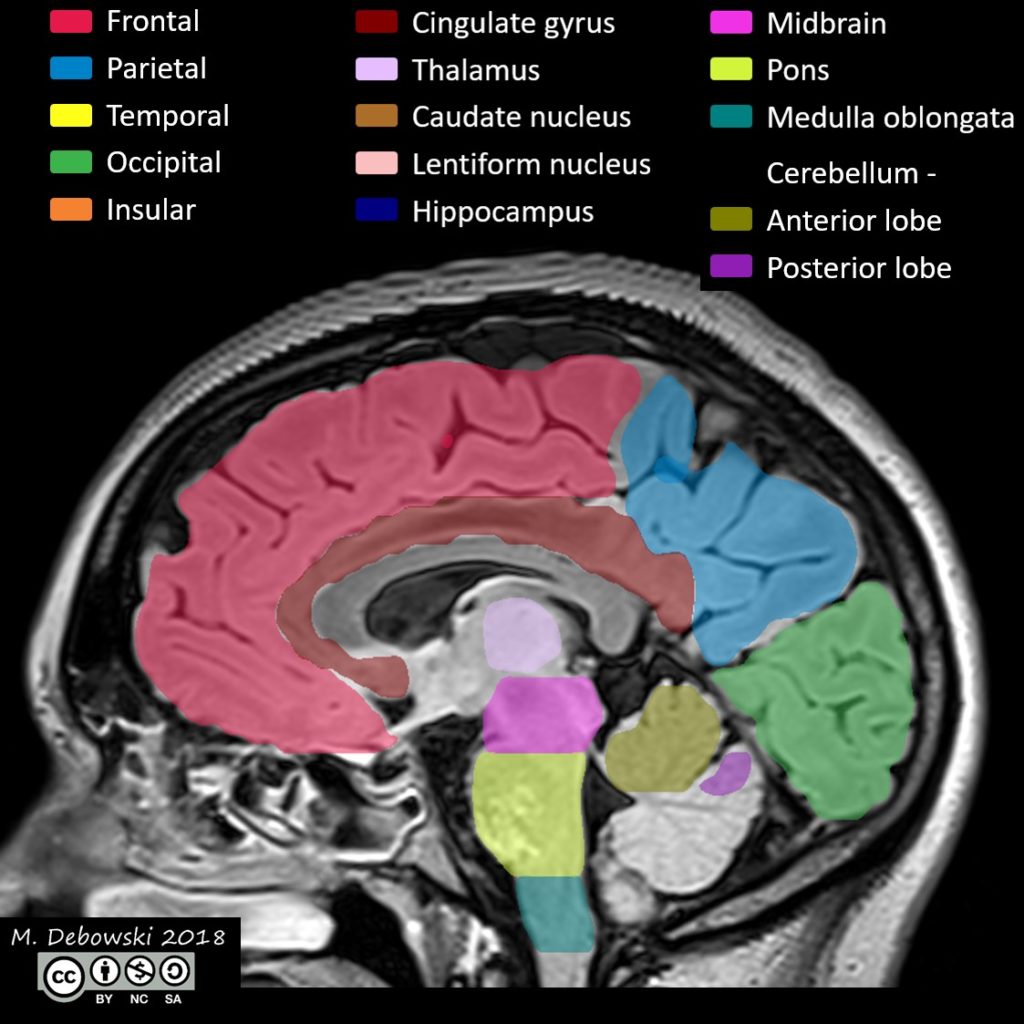
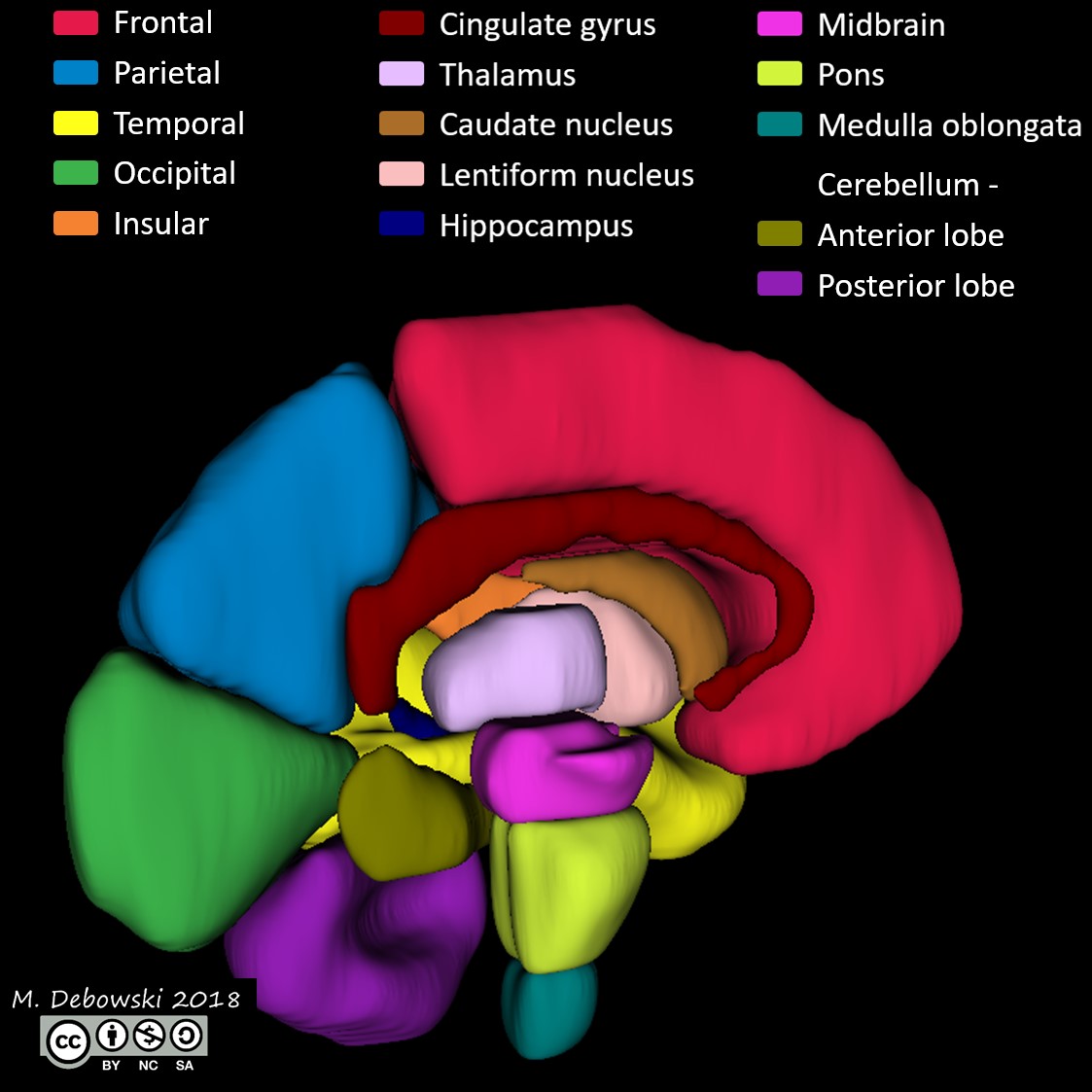
References
Jumah, F. R., & Dossani, R. H. (2019). Neuroanatomy, cingulate cortex.
van Heukelum, S., Mars, R. B., Guthrie, M., Buitelaar, J. K., Beckmann, C. F., Tiesinga, P. H., … & Havenith, M. N. (2020). Where is cingulate cortex? A cross-species view. Trends in Neurosciences, 43(5), 285-299.
Wikipedia contributors. (2024, January 22). Cingulate cortex. In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 11:18, February 26, 2024, from https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Cingulate_cortex&oldid=1197958812